网络编程
1. InetAddress 类的使用
实现网络通信需要解决的两个问题
(1)如何准确地定位互联网上的一台或多台主机;
(2)如何实现可靠而高效的数据传输。
网络通信(就对应着上面的两个问题)
要素一:使用 IP 地址,定位网络中的主机;
要素二:遵循相关的网络通信协议。
针对要素一
(1)IP:一个 IP 地址,对应着网络中的一台主机。如“192.168.10.16”、“127.0.0.1” --- 本地回路地址。
使用 InetAddress 类来代表 IP,一个 InetAdress 类的对象,就代表着一个具体的 IP 地址。
(2)如何实现 InetAdress 类
①getByName(String hostName) ②getLocalHost();
(3)两个方法的使用
getHostName() / getHostAddress()
(4)域名:www.baidu.com
域名解析:域名容易记忆,当在连接网络时,输入一个主机的域名之后,域名服务器(DNS)负责将域名转化为 IP 地址,这样才能和主机建立连接)。
端口号的使用
端口号标识正在计算机中运行的进程(程序)
注意:不同的进程对应不同的端口号
常见的端口号:http:80 tomcat:8080 mysql:3306 oracle:1521 等。
针对要素二
使用网络通信协议
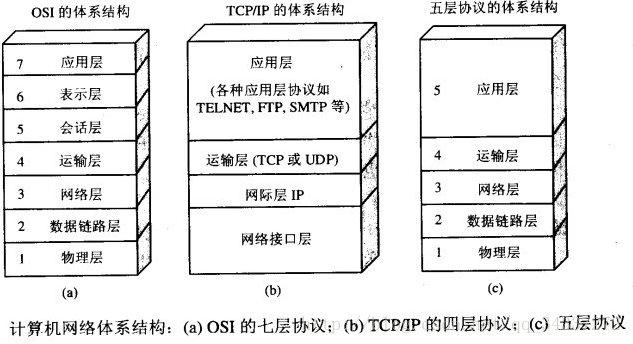
network-protocol TCP 与 UDP 协议的区别
TCP 协议:
(1)使用 TCP 协议前,须先建立 TCP 连接,形成传输数据通道;
(2)传输前,采用“三次握手”的方式,是可靠的;
(3)TCP 协议进行通信的两个应用进程:客户端、服务端;
(4)在连接中可进行大数据量的传输;
(5)传输完毕,需释放已建立的连接,效率低。
UDP 协议:
(1)将数据、源、目的封装成数据包,不需要建立连接;
(2)每个数据报的大小限制在 64k 内;
(3)因无需连接,故是不可靠的;
(4)发送数据结束时无需释放资源,速度快。
2. TCP 网络编程
// 客户端
@Test
public void client() {
OutputStream os = null;
Socket socket = null;
FileInputStream fis = null;
// ***************************************
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
InputStream is = null;
try {
// 1.创建Socket对象,指明服务器的ip和端口号
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
//InetAddress address1 = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
socket = new Socket(address,7788);
fis = new FileInputStream("p1.jpg");
// 2.获取一个输入流,用于输出数据
os = socket.getOutputStream();
// 3.写出数据的操作
byte[] buffer1 = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buffer1)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer1,0,len);
}
// 使用IO流进行网络数据的传输是阻塞式的,需要手动调用shutdownOutput/shutdownInput()方法“告知”哪里是数据传输结束的点
socket.shutdownOutput();
// ***********************************************************
// 读取反馈回来的数据
is = socket.getInputStream();
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer2 = new byte[1024];
while((len = is.read(buffer2)) != -1) {
baos.write(buffer2,0,len);
}
System.out.print(baos);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4.资源的关闭
if(os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket != null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(baos != null) {
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 服务端
@Test
public void server() {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
// *********************************
OutputStream os = null;
// 1.创建服务器端的ServerSocket,指明自己的端口号
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(7788);
// 2.调用accept():表示接受来自客户端的socket
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
// 3.获取输入流
is = socket.getInputStream();
// 4.读取输入流中的数据
// baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();// 数据写出到一个字节数组作为返回值返回,避免读取文本时出现乱码
fos = new FileOutputStream("p2.jpg");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("图片传输完成");
// *************************************************************************
// 服务器发送反馈给客户端
os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("我收到了".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 5.资源的关闭
if(serverSocket != null) {
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(baos != null) {
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}3. UDP 网络编程
发送端只管发送,不管结果是否如何,是不可靠的网络传输方式。
@Test
public void sender() {
DatagramSocket ds = null;
DatagramPacket dp = null;
try {
// 1.创建DatagramSocket的对象
ds = new DatagramSocket();
// 2.创建要发送的数据报DatagramPacket对象,指明内容(byte[])、长度、接收端IP地址、端口号
byte[] buf = "使用UDP方式进行发送的导弹".getBytes();
dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 5566);
// 3.发送数据报
ds.send(dp);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(ds != null) {
ds.close();
}
}
}
@Test
public void receiver() {
DatagramSocket ds = null;
DatagramPacket dp = null;
try {
// 1.创建DatagramSocket对象,指明端口号
ds = new DatagramSocket(5566);
// 2.创建DatagramPacket对象,指明内容(byte[]),以及接收的字节数组的下标范围
byte[] buf = new byte[200];
dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,0,buf.length);
// 3.接收数据报
ds.receive(dp);
System.out.println(new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength()));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(ds != null) {
ds.close();
}
}
}4. URL 网络编程
URL:(Uniform Resource Locator)
统一资源定位符,它表示 Internet 上某一资源的地址。
比如:http://127.0.0.1:8080/examples/p1.jpg
协议 主机 端口号 web工程 文件
如何实例化
URL url = new URL(“http://127.0.0.1:8080/examples/p1.jpg”);- 常见方法
public String getProtocol() 获取该URL的协议名
public String getHost() 获取该URL的主机名
public String getPort() 获取该URL的端口号
public String getPath() 获取该URL的文件路径
public String getFile() 获取该URL的文件名
public String getQuery() 获取该URL的查询名- 可以读取、下载对应的 url 资源
@Test
public void test() {
HttpURLConnection conn = null;
InputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
URL url;
try {
url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/examples/p1.jpg");
conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.connect();
is = conn.getInputStream();
fos = new FileOutputStream("p3.jpg");
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(buf,0,len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(conn != null) {
conn.disconnect();
}
if(is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}